Date:2019-12-26 Author:
CWDM and PSM Basics
Before the comparison, it's necessary to go through some basics of CWDM and PSM:QSFP-40G-LR4 CWDM Transceiver
QSFP-40G-LR4 CWDM transceiver commonly refers to the QSFP+ 40G LR4 transceiver. With a duplex LC interface, QSFP+ CWDM LR4 is compliant to 40GBASE-LR4 of the IEEE P802.3ba standard. It contains four unbiased transmit and receive channels, with each channel carrying a 10G optical transmission. The maximum transmission distance of this QSFP+ transceiver type is 10 km. To minimize the optical dispersion in the long-haul system, the single mode fiber (SMF) has to be used.
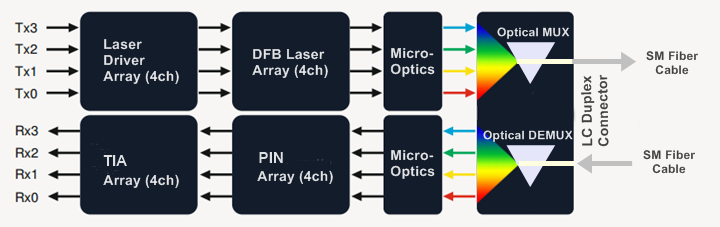
The central wavelengths of the 4 CWDM channels are 1271, 1291, 1311 and 1331 nm, which comply with CWDM wavelength grid defined by ITU-T G694.2. Each wavelength channel is collected by a discrete photodiode and output as electric data after being amplified by a trans-impedance amplifier (TIA).
QSFP-40G-LR4 PSM Transceiver
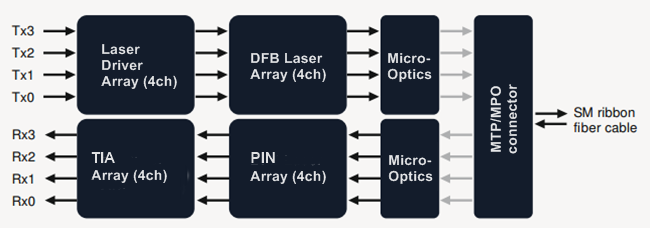
QSFP-40G-LR4 PSM is also named as QSFP-40G-PLR4 by some vendors like Arista and Cloudopitcs. Equipped with an MTP/MPO fiber ribbon interface, the LR4 PSM QSFP+ transceiver offers 4 independent transmit and receive lanes, each capable of 10G operation up to 10 km over single mode fiber.
QSFP-40G-LR4 PSM works in a way that the transmitter module accepts electrical input signals compatible with common mode logic (CML) levels. Then the receiver module converts parallel input signals via a photodetector array into output signals. The output signals of the receive module are also voltage compatible with CML levels. Usually, there are guide pins inside the MTP/MPO interface receptacle for proper channel to channel alignment. In that case, when users plug an optical cable with the MTP/MPO connector into a QSFP+ transceiver receptacle, the cable cannot be twisted in case of alignment failure.
QSFP-40G-LR4 CWDM vs. PSM: What's the Difference?
As 40G QSFP+ transceivers, both 40G LR4 CWDM and PSM are used for long-distance transmission. However, in the aspects of optical transmitter (optical Tx), optical MUX/DEMUX, interface, and fiber, they have different features as listed in the following table.
| Parameter | 40G LR4 CWDM | 40G LR4 PSM |
| Optical Tx | 4 uncooled 1300nm CWDM directly-modulated lasers (20nm wavelength spacing) | 4 integrated silicon photonic modulators and one CW laser (uncooled 1300nm DFB laser) |
| Optical MUX/DEMUX | Yes | No |
| Interface | Duplex LC | MTP/MPO fiber ribbon |
| Fiber | 2 single-mode fibers | MTP/MPO fiber ribbon |
FAQs About QSFP-40G-LR4 CWDM/PSM
Can QSFP-40G-LR4 CWDM and PSM Transceivers Be Used for 4x10G?
It depends on your QSFP+ transceiver type. When you use the QSFP-40G-LR4 CWDM transceiver, it cannot be split into 4x10G. That's because it uses 4 wavelengths on a pair of single mode fiber with LC duplex interface, and does not allow itself to split into 4 pairs without substantial complexity to split out the wavelengths. However, if you use a QSFP-40G-LR4 PSM transceiver, the answer will be different. 40GBASE-LR4 PSM QSFP+ transceiver can be used for 4x10G, because it uses parallel (ribbon) fiber with MTP/MPO interface, which allows the creation of 4 fiber pairs.
What's the Difference Between QSFP+ PSM IR4 and 40G QSFP+ PSM LR4 Transceivers?
These two QSFP+ transceivers are both the integrated four-channel optical transceivers with MTP/MPO fiber ribbon interfaces. The only difference lies in their supported transmission distance. 40G PSM LR4 is used to support a transmission distance no further than 10 km while 40G PSM IR4 is 1.4 km.
What Are the Differences Between QSFP+ CWDM LR4 and LX4/ ER4 Transceivers?
Their differences are mainly caused by their supported cables and transmission distances. QSFP-40G-LR4 CWDM is used to support up to 10km link distance over the single mode cable. LX4 CWDM QSFP+ transceiver is designed to support up to 2km (SMF) and 150m (MMF) optical communication applications. And QSFP+ 40G ER4 CWDM transceiver supports the link length of up to 40 km over SMF with the duplex LC interface.
 Copyright © 2019 cloudoptics. All Rights Reserved - Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2019 cloudoptics. All Rights Reserved - Privacy PolicyEmail: sales@cloudoptics.net